The transition to EVs is being primarily driven by rising technical improvement in vehicle electrification, spanning from battery to power electronics, charging to vehicle engineering, as the world prepares for the E-Mobility revolution and the adoption of sustainable forms of transportation.
The “On-Board Charger” (OBC) technology that is included with the electric car enables plug-in hybrid (PHEV) and battery electric vehicles (BEV) to charge their vehicles using AC power or anywhere there is an AC power source, whether at home or in public spaces.
On-Board Charger is effectively in charge of transforming grid-supplied AC power to the DC voltage that is needed to charge the vehicle’s battery pack. Besides, It also looks after charging the battery pack in addition to providing charge monitoring and safety.
Embitel, with an experience in the automotive industry spanning over 15 years, helps in custom design and development of On-Board Charger solutions for EVs.
Top 3 challenges faced by OEMs/Brands while designing On-Board Charger

The energy efficiency and power density

The unit needs to be “small and compact”

The design maturity and thermal management
Keeping in mind the challenges stated above, Embitel Provides On-Board Charger solutions as per National and International standards, compatible with TYPE 1, Type 2, and Type 3 Charging stations.
Our On-Board Charger Solutions Come With the Following Features
- Microcontroller board (based upon the requirement)
- CAN communication transmission rate 250-KBPS
- Implementation of active power decoupling for improving reliability and power density
- Input voltage – 150 to 270 Vac
- Output power – ≤ 22 kW (or more based on the requirement)
- SAE J1772 (Type 1 / Type 2 / Bharat AC-001 connector) standards for power communication
- Power factor greater than 95% for all load condition
- High Power density
- Peak efficiency 94%
- Power flow: V2G (optional Bi-directional – G2V or HV to LV)
- Compliant with global EV standards and Configurable with all vehicle platforms
- Functional safety compliances
On-Board Charger Architecture and Block Diagram
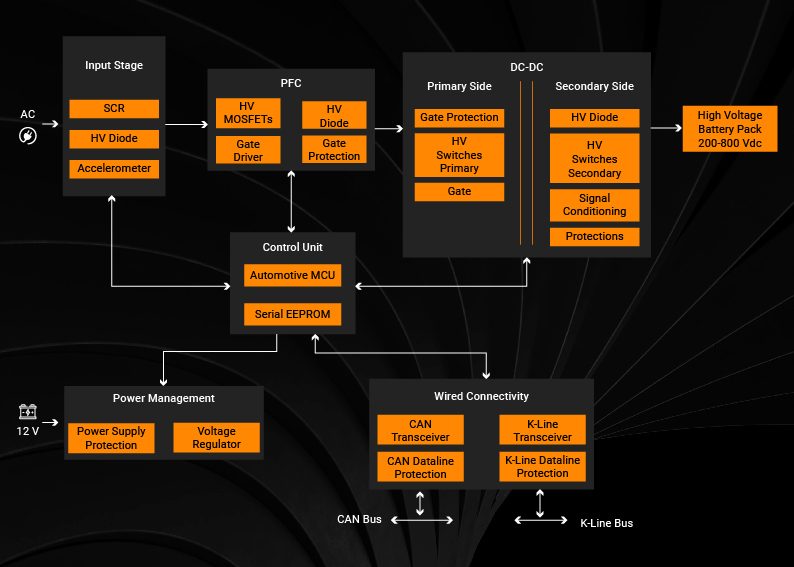
Product Engineering Services for On-Board Charger Solution Development

Power Devices, Passive element and Microcontroller:
- SIC MOSFETs technology for high efficiency and high frequency operation.
- Distributed air gap sendust cores for inductors for lower losses and better temperature handling.
- AUTOSAR based Software.
- Firmware, software and Control algorithms development and implementation.

Enclosure Design:
- Modular and IP65 rated design of enclosure
- Smart packaging of all electronic components to optimize the thermal management and accessibility
- CFD analysis for better thermal management

Verification and Validation:
- MATLAB simulation of power converter and control loop algorithm verification
- Software unit testing
- Software integration testing
- Software qualification test
- System integration and qualification testing

Topologies:
- Interleaved PFC for AFE converter stage
- Phase shift full bridge ZVS converter for DC-DC stage
- LLC converter for Auxiliary converter stage
- Active power De-Coupling

