ISO 26262 Compliant LIN Protocol Software
ASIL D ready LIN protocol software to power ECU communication for safety-critical components






Enabling Low-Cost ECU Communication
Embitel’s LIN Protocol Software
Embitel offers a ready-to-deploy LIN protocol software package. Our LIN stack is compliant to LIN 2.0, LIN 2.1, LIN 2.2, ISO17987 and SAE2602 standards. With our production-grade LIN stack, you can implement customized LIN Master and LIN Slave solutions.
Our LIN protocol stack is ASIL D ready! It can be deployed for ASIL D grade automotive solutions to enable highest level of functional safety.
We offer this LIN Protocol stack under a one-time licensing fee model. This engagement model makes the LIN stack highly beneficial for our customers.
LIN BUS Protocol Stack: Details of the Software Architecture
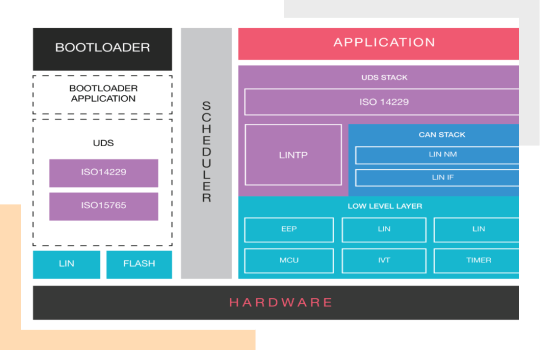
- LIN Device Drivers: It facilitates the access to the hardware resources and offers a hardware independent API to the upper layer. We develop LIN driver for the specific microcontroller as per the safety requirements of the customer.
- LIN Hardware Abstraction Layer: Consists of LIN Interface and LIN TP Layer; Responsible for hardware abstraction, error handling and transport layer software services for diagnostics.
- LIN Network Management: Coordinates the transition between normal operation and bus-sleep mode of the network.
Features of Our LIN Protocol Stack Solution
ASIL D Ready
- LIN network management (LIN NM) and interface layer (LIN IF) have been developed as per ISO 26262 guidelines following ASIL D recommendations.
- Our LIN protocol stack can be integrated to ASIL D category ECU development programs.
LIN Stack License Model
- We offer our industry recognized LIN protocol software under a one-time licensing fee model.
- Terms & conditions regarding IP rights and source code ownership are completely transparent and fully aligned with the customer’s requirements and vision.
LIN Master / Slave Architecture
- The LIN subnet is based on a master-slave architecture and we have partnered with our customers to deliver a customized LIN Master and LIN Slave solutions.
- Within the In-Vehicle Network, LIN Master is integrated with Master ECU (which is part of Body Control Module).
- LIN Master ensures robust communication and control of the LIN Slave nodes
LDF to auto-code generator Tool
- MISRA C compliant auto-code generation for LIN Interface configuration in lesser time as compared to manual method (3-4 week)
- This saving in efforts translates into reduction time-to-market and thus development cost.
LIN Protocol Stack Use-Cases
- LIN protocol stack implementation for sun-roof systems, DC DC converter, wiper, power-window etc.
- LIN protocol based ECU re-programming (Bootloader) over UDS.
- Integration of UDS over LIN TP.
LIN Bus Protocol Stack Integration, Configuration and Testing Service Offerings

Development and Integration of LIN Driver
- Device Drivers development for the LIN Slave microcontroller
- Device Drivers development for LIN Master microcontroller
- Reusable device drivers to ensure reduced development time and cost
- Support for driver integration for most MCU families

Node Configuration, LIN Network Management and LIN TP Configuration
- Support for Static and Dynamic Configuration of Nodes (ECUs)
- Already integrated Read/write to the stack function
- Sleep/Wake up functionality for the nodes
- Support for segmentation of large data packets over LIN TP

Development and Configuration of LIN Master
- Configuration of the Scheduler Table based on SWRS and LDF files
- Support for Unconditional, Event, Sporadic and Diagnostics frame
- Skeleton code for Scheduler Table
- Integration with the end-user application and HAL
- Algorithm development for Scheduler Table

LIN Bus Protocol Stack Support and Maintenance Services
- Documentation Support: Low-level design and High-level design documents
- LIN conformance test using Vector Tools. This ensures robustness of Data Link Layer
- Unit, Integration and Functional testing services
- Support for MISRA C Report creation
Development and Configuration of LIN Hardware Abstraction Layer
- Tx and Rx message configuration from LIN Description File (LDF)
- Support for both tool based and manual configuration
- Proprietary LDF to auto-code generation tool
- Configuration for Software Filtering
- Vector tool based LDF generation from excel sheet
- Configurable HAL standard code is part of the stack package

Support for upgradation to LIN 2.2
- Evaluation of existing LIN network to analyze limitations, compatibility and other issues that need to be addressed
- Support for new network design or changes in existing LIN network based on the analysis.
- Integration of LIN 2.2 by updating the previous version of LIN protocol
- Support for thorough testing and validation of the network after integration of LIN 2.2 protocol to ensure performance and reliability of the nodes.

ISO 26262 Compliant with ASIL D Level Safety
- LIN TP, LIN NM, LIN interface layer and LIN Node service layers are ASIL D ready
- Safety guidelines and methodologies enlisted in Part-6 of ISO 26262 standard (Table-1 to 15) are rigorously followed.
- E2E profiles and CRC library are implemented for data integrity
200+
customers supported since 2010
100+
scalable and reusable Bootloader platforms delivered
30%
quicker time-to-market enabled
95%
lesser development time with PC-based automation tools
Embitel’s Advantage
ISO 26262 Compliance
We have developed our LIN protocol as an SEooC (Safety element out of context). The development process follows ISO 26262 guidelines mandated for SEooC development.
Industry-wide Recognition
We have integrated LIN stack for several production programs across the globe. The extensive experience gives us an edge in the implementation of on-board diagnostics for automotive use-cases.
CMMi Level 3 Certified
As a CMMI level 3 certified organization, we have a robust process model in place. This ensures that the LIN stack along with other stacks are reliable, bug-free and efficient.
Configuration & Integration Support
Our LIN protocol software is designed to be fully configurable as per project specifications. We provide support for configuration of LIN Stack based on LDF .
Support for After-market Solutions
Development, testing and maintenance support for after-Market Products for Telematics, ADAS, remote vehicle diagnostic applications.
ISO 26262 Compliance
We have developed our LIN protocol as an SEooC (Safety element out of context). The development process follows ISO 26262 guidelines mandated for SEooC development.
Know more about our LIN protocol software business model, features,
use-cases, and technical specifications.
FAQs About LIN BUS Protocol Stack Solution
Ans. The layered architecture of our LIN Protocol stack includes:
- Low-level drivers (LIN, MCU, EEP, IVT, Timer)
- LIN Bus Protocol Stack (LIN Network Management and LIN Interface)
- LIN TP Layer
- UDS Stack (ISO 14229)
- Application Layer
- Bootloader Application
- UDS (ISO14229) Based Bootloader
- LIN Master and Slave Driver, in compliance with LIN 2.1 specifications (SAE J2602)
- Interrupt based data handling (both Transmission and Reception).
- Error handling mechanism is part of the LIN driver software.
- LN IF handles both Tx and Rx messages.
- Schedule table will be part of LIN Interface
- Tx and Rx messages will be configured in configuration (*.c, *.h) files.
- Signals will be extracted as per LDF file and sent to application layer via APIs
- Handles multi-packet transmission and reception
Ans. LIN Drivers are developed for the specific microcontroller used in the automotive application. All other modules of the LIN software are hardware agnostic.
We have expertise in developing LIN drivers for all the widely used MCU families. This includes Renesas, TI, Fujistsu and others.
Ans. Our automotive team has delivered several LIN bus protocol stack projects to customers from across US, Europe and India.
We can share the detailed case studies of the projects and related information, once we sign the Non-disclosure agreement.
Ans. Yes. As per our Service Level Agreement (SLA) for the LIN bus protocol Stack, we will provide the software configuration and integration services, along with the LIN bus software stack license.
The integration and configuration services will take care of both low-level drivers as well as the application-level integration.
Ans. We perform various tests in the course of LIN software stack development. Prior to the final project delivery, our LIN bus protocol stack solution undergoes the following testing procedures:
- Unit level Testing
- Functional Testing
- Data Link Layer Compliance testing, using Vector Testing Tools
Ans. Whether to use the manual method or the PC based tool, for the conversion from LDF file to configuration file code, will depend on the size of the file.
If there are considerable numbers of Tx and Rx messages for configuration, we will prefer to use our proprietary PC based auto-code generator tool.
Ans. The PC-based tool runs on Windows OS and has been developed by our automotive team. It reads the LDF file and converts it into configuration files instantly.
Our in-house LDF to auto code generation tool has the following benefits:
-
Designed for generating MISRA C compliant configuration files.
-
Code generation is much faster than the manual method (Manual Method takes 2-3 weeks depending on LDF file size).
-
It not only saves the time but also cuts down the cost.
Ans. Our LIN bus software stack is light-weight in size. The size of flash memory is 6 kB and RAM size is 1 kB. The RAM size could go higher depending on the size of the configuration file.
Ans. Yes, Our LIN bus protocol stack is completely modular. There are no global variables exchange between the programs files and every functionality is invoked with the help of specific APIs.
Modularity makes the LIN software stack light-weight and also easy to deploy in number of production programs, without any compatibility issue.
Ans. We offer separate stack solutions for both LIN Master and LIN slave. As LIN is not a broadcast protocol, the LIN master is tasked to initiate the command and the slave has to act on it.
Depending on the project specifications, we will deliver LIN master, LIN slave or both.
Ans. High-Level Design Document and Low-Level Design Document, will be a part of the LIN bus software stack package. In addition to that, we will also provide Functional Test Plan & Report and MISRA compliance Report.
These documents contain every detail you may need to make some enhancements to the stacks or to integrate the stack solution in multiple production projects.
Ans. We offer complete support for upgrade to LIN 2.2 from its LIN’s previous versions. Here’s a snapshot of services we provide to help you upgrade to the latest version of LIN i.e LIN 2.2.
Consulting: A LIN 2.2 upgrade can be a complex process, so consulting services can help organizations determine the best approach based on their specific needs and infrastructure.
Implementation: Once a plan has been developed, our LIN 2.2 implementation services can help you carry out the LIN 2.2 upgrade efficiently and effectively.
Testing and Validation: Before and after the upgrade, we test and validate the new LIN 2.2 system to ensure that it’s functioning correctly and meeting performance expectations.
Support and Maintenance: Even after the upgrade is complete we offer ongoing support and maintenance services that may be necessary to keep the LIN 2.2 system running smoothly and address any issues that arise.
Ans. Our LIN Stack comes in both QM and ASIL D ready variant. Our ASIL D LIN protocol stack variant has been built as per the most stringent ASIL D guidelines. The E2E profiles aided with CRC library make our stack solution an unbreachable fortress. Every data bit that is communicated through the layers of our LIN stack is validated on multiple counts. We have already implemented our LIN stack for multiple ISO 26262 compliant automotive programs.
Knowledge bytes
- What is Local Interconnect Network (LIN) BUS Protocol Stack?
LIN protocol is a sub-network deployed in both passenger and off-road vehicles. Unlike CAN, which is a broadcast protocol, LIN is a master/slave communication standard.
Simpler functionalities like wiper, mirror control and washer etc. are usually handled by LIN network.
The LIN master ECU is integrated with the body control module, from where it initiates the command. The LIN master nodes will receive the command over LIN network and act accordingly.
LIN Slave nodes don’t communicate with other networks, unless initiated by the LIN master.
- What makes Local Interconnect Network (LIN) important when CAN already handles in-vehicle networking?
Adding too many nodes (ECUs) to the network causes Network BUS slow down. To prevent this, a LIN sub-network is designed. The body control module usually acts as a gateway between the main network (CAN Bus) and the subnets (LIN Bus)
LIN Bus is a single wire network best suited for small applications like wiper and washer etc. Using CAN for such application lead to increase in the software and hardware cost.
- What are the advantages of upgrading your vehicle network solutions to LIN 2.2?
LIN 2.2 is the latest version of LIN bus protocol released in 2010. It is also the most implemented version of LIN protocol as it has several advantages compared to its previous versions.
LIN 2.2 offers several advantages over previous versions of the LIN protocol, including:
Increased speed: LIN 2.2 operates at a maximum speed of 20 kbps, which is twice as fast as the previous LIN 2.0 and 2.1 versions.
Improved scalability: LIN 2.2 supports up to 16 slave nodes on a network, which is four times the number of slave nodes supported by previous versions of the protocol.
Enhanced reliability: LIN 2.2 introduces improved error detection and correction mechanisms, which help to ensure reliable data transmission even in noisy environments.
More robust network management: The LIN 2.2 protocol includes several new features for network management, such as improved wakeup functionality and support for network synchronization.
Lower power consumption: The LIN 2.2 protocol includes several new features for reducing power consumption, including a sleep mode for slave nodes and reduced idle current consumption.
- How to build an ISO 26262 compliant LIN protocol stack which is ASIL D ready?
The idea to develop a LIN protocol stack as per ISO 26262 is essentially building a safety element out of context (SEOOC). In such a scenario, the safety requirements, safety goals etc. are not determined through HARA, instead they are assumed at component level.
These assumed safety requirements should be aligned with typical safety goals for LIN communication in automotive systems. Part-6 of ISO 26262 standard gives a detailed guideline along with testing and coding methodologies to be implemented. Since, the target is to develop an ASIL D LIN protocol stack, all these guidelines summarized in close to 15 tables must be followed rigorously.
In addition, E2E profiles are implemented to ensure data integrity and reliability during communication.


