e-Health is a conspicuous buzzword in the healthcare industry today. It is essentially the use of communication technologies and data transfer for the delivery of remote healthcare.
eHealth is still in its nascent stages as far as adoption is concerned. Nevertheless, it carries great promises such as improved efficiency in healthcare, enhanced quality and cost reduction, empowerment of patients, and extension of healthcare beyond the current boundaries it is restricted to.
e-Health is a combination of diverse services such as e-learning, health informatics and telemedicine, to name a few. In this article, we explore how the Internet of Things (IoT) can provide a robust technology framework for enabling telemedicine.
An Overview of Telemedicine Services
Telemedicine can be defined as the delivery of healthcare services by professionals using various technologies. This mitigates the limitations of distance, as information related to diagnosis, treatment, prevention of ailments, etc. is exchanged between the doctor and the patient through electronic means.
The main advantage of telemedicine is its ability to bring health services closer to patients living in remote locations where it is otherwise difficult to obtain quality healthcare. In the recent years, telemedicine is found to improve the efficiency of healthcare services, as it enables sharing of resources (medical consultations and patient health records) across multiple remote locations.
Some of the services included in telemedicine are:
- Remote assistance for teleconsultations, diagnosis, follow-up checks and continuous treatment plans.
- Hospital administrative services such as laboratory testing, billing, resolution of issues, etc.
- Telemonitoring is the usage of technology to transmit patient data between individuals in geographically different locations. This helps both doctors and primary caregivers monitor patients through electronic devices. Telemonitoring services facilitate continued care of patients at home. This reduces hospital stays and also provides them more control over the management of their diseases.
What are the Main Applications of Telemedicine?
As indicated above, telemedicine is applied in remote patient healthcare. Patients who are unable to travel to hospitals or those residing in remote locations without quality healthcare institutions find immense benefit from it. It is also considered by patients who seek second opinions for their medical diagnoses.
Telemedicine, a salient example of IoT in healthcare, facilitates the exchange of a wide range of information between doctors and patients through connected devices and the internet. This includes:
- Diagnostic x-ray images
- Clinical laboratory data or patient history details
- Diagnosis of cardiovascular diseases
- Tele-dermatology image transmission and video conference
Challenges in Implementation of Telemedicine
Some of the common challenges encountered while trying to implement a telemedicine service can be summarized as follows:
- Stakeholder engagement – It is found that people are, more often than not, resistant to a change in the conventional mode of providing/obtaining healthcare services. The absence of an emotional bond formation between the healthcare expert and patient and unfamiliarity with the advancements in eHealth technology are some factors that contribute to this resistance.
- Organizational limitations – In order to implement a telemedicine model, it is necessary to redesign the existing models in healthcare organizations. There may also be a need to redefine roles and responsibilities. Implementation costs and funding needs are other factors that fall under this category.
- Technological factors – It is found that the lack of infrastructure and skills for managing the technology for telemedicine is a key barrier to its implementation. In this context, it is important for healthcare organizations to collaborate with a reliable IoT partner company with experience in the domain.
Apart from the above factors, it is crucial to establish a well-defined evaluation methodology for the deployment. The actual deployment results may differ from the research findings of the past. Hence, the deployment should be considered as an iterative activity wherein the outcomes of each stage may result in further process flow changes.
Framework for Implementation of Technology for Telemedicine
When we scan through the challenges listed above, we find that technological factors are a crucial deterrent in the implementation of a telemedicine framework. In the recent past, the advent of cost-effective web and mobile applications have accelerated the growth of remote healthcare.
Ideally, telemedicine technology should be user-friendly, available, and customizable. In other words, the hardware of devices should have a streamlined form factor that appeals to the patients and healthcare professionals alike.
The technology should also be easy to integrate with the existing healthcare infrastructure. Another aspect to be considered is the training that needs to be imparted to users for smooth functioning of the setup.
Healthcare organizations can leverage the power of IoT to develop telemedicine applications that are robust, cost-effective and available. In the implementation of a telemedicine framework based on IoT, the following components play a significant role:
- Healthcare devices – Examples of IoT-enabled healthcare devices are wearable health monitoring apps used by patients. These healthcare devices monitor the vitals of the user and record data over a period of time. Some of these devices can also assist in prediction of impending diseases based on the overall health of the user.
- Cloud application – The data collected by healthcare devices may be sent to an IoT cloud platform from where the information is consolidated by the healthcare provider. This data can subsequently be transmitted to IoT applications used by healthcare facilities for patient monitoring purposes. This information yields valuable insights for the future treatment of patients.
Patient monitoring is not the only purpose of deploying an IoT-powered device. Hospitals may install IoT sensors on wheelchairs, nebulizers, defibrillators and other medical equipment so that these can be tracked in real time. The location of medical practitioners associated with the hospital can also be monitored this way.
IoT-based Telemedicine App Development
Telemedicine apps can be segregated into the following types:
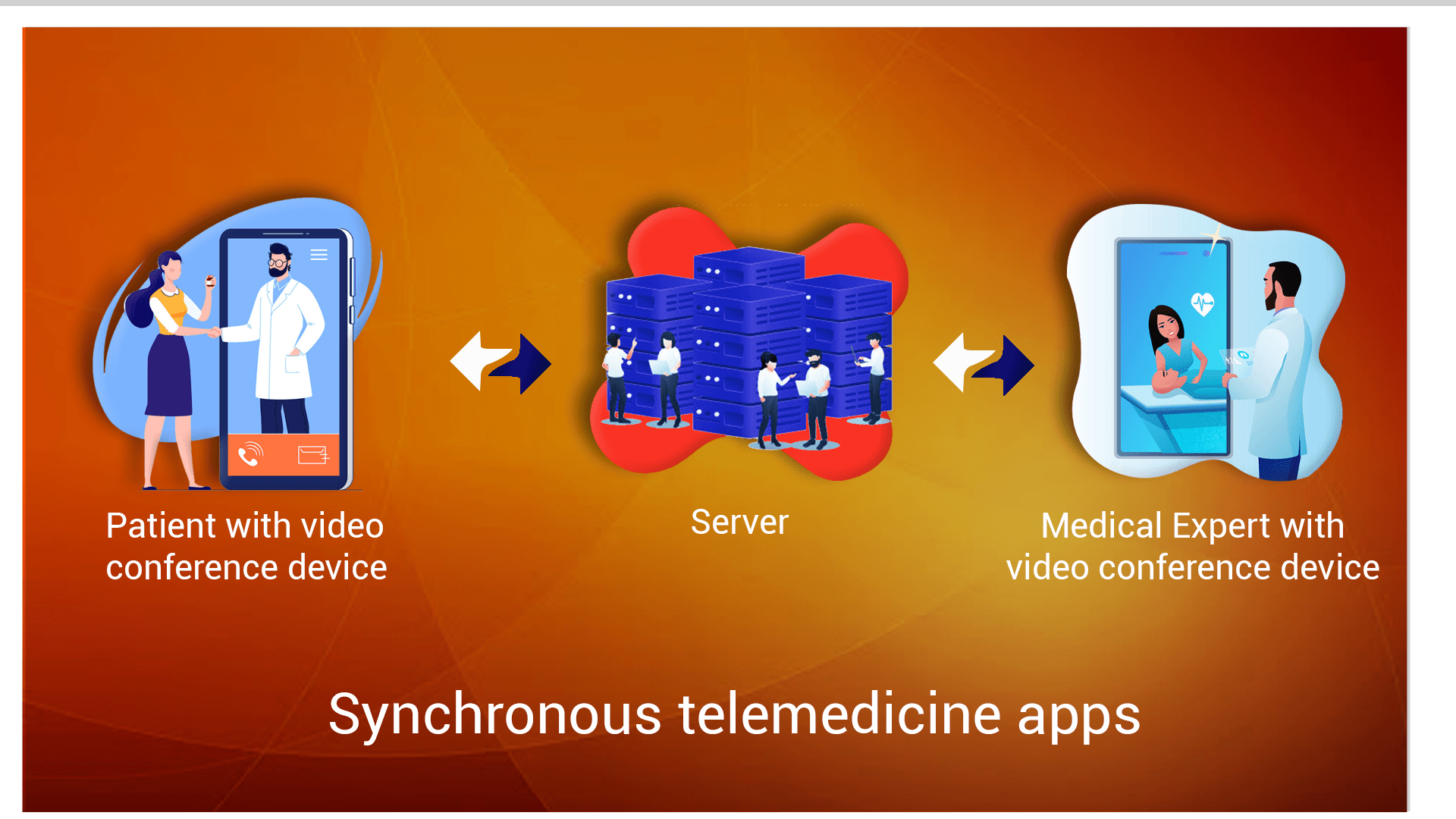
- Synchronous telemedicine apps – Also referred to as interactive telemedicine systems, these applications provide real-time interactions between doctors and patients through telecommunications. The live conferencing feature in these apps helps in sharing the patient’s ailments and conditions effectively, hence facilitating improved level of interactions.
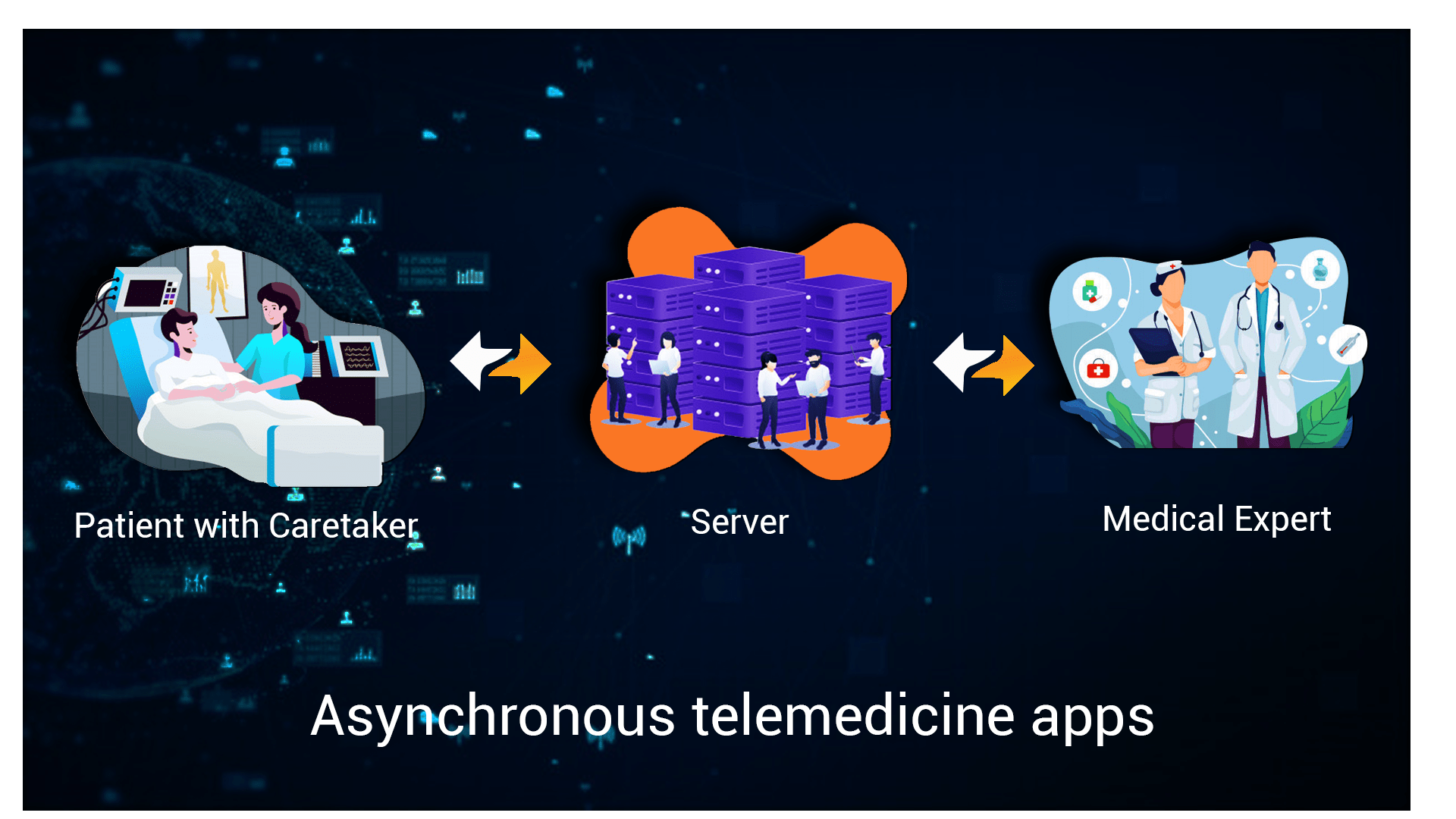
- Asynchronous telemedicine apps – These apps collect the patient’s medical images and records and share with the doctor/healthcare facility at a suitable time for analysis. The collection of data can be done by a primary care provider if the patient is unable to do so himself. These apps do not mandate the simultaneous attention of both parties for the consultation.
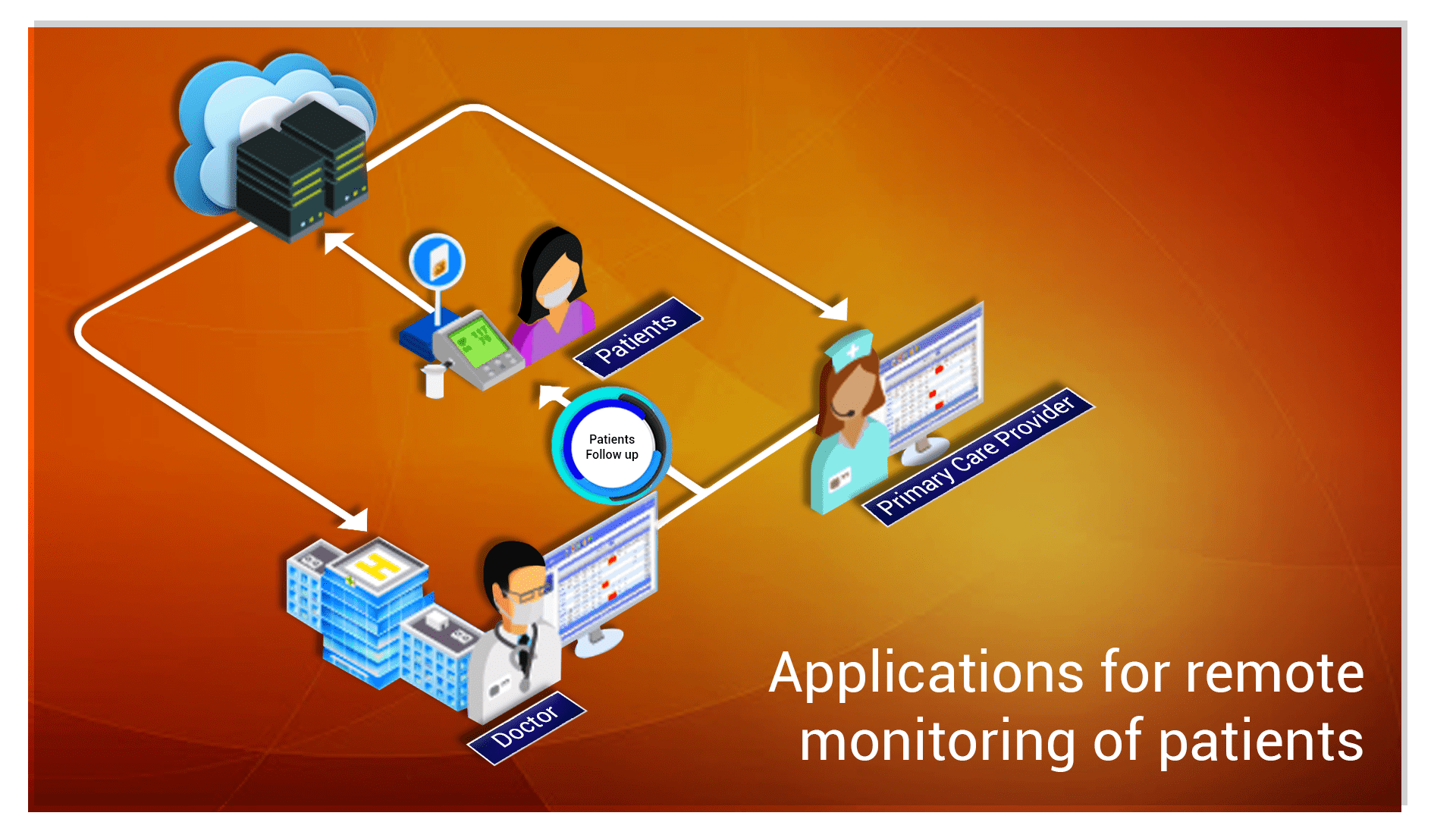
Applications for remote monitoring of patients – Remote patient monitoring or telemonitoring is usually utilized for keeping track of the health conditions of elderly patients. Patients use devices fitted with sensors that transmit signals through the cloud application/server. The doctor and primary care providers can monitor the signals from patients remotely through the telemedicine app.
Mobile Health applications – The concept of Mobile Health (M-Health) includes smart mobile applications that transmit data through powerful mobile data network. The doctor and patient can access the medical records asynchronously.
Key Requirements for the Successful Deployment of a Telemedicine App
- Device and network selection – Selection of the right type of device hardware, network connectivity and communication protocols are vital in determining the most suitable telemedicine app for your requirements. While deciding on the hardware, security in data transmission and storage needs special focus.
- Rigorous testing before implementation – It is important to elaborately test the telemedicine app before launch, as it would otherwise incur unplanned logistic expenses.
- Predictive maintenance – IoT-powered telemedicine infrastructure can be fortified with predictive maintenance capabilities to minimize downtime and improve efficiency.
Basic Features of a Telemedicine App
A telemedicine app should have the following features to cater to the needs of patients:
- Easy registration
- Concise patient profile
- Search functionality to connect to suitable physicians
- Communication (audio, video, text chat) facility
- Payment gateway
- Appointments and notifications
- Review and rating
- Emergency call facility
- Insurance module
As far as the healthcare provider is concerned, the following features would be beneficial in a telemedicine app:
- Concise doctor profile
- Calendar and schedules
- Patient tracking
- Prescription management
- Dashboards showing status of treatments
- Data storage in cloud
- Video/audio session recording
- Pharmacy stock details
Concluding Thoughts
Telemedicine has evolved to be a promising healthcare service that provides several benefits to both the doctors and patients. Apart from facilitating easy availability of quality healthcare, it offers an amplified degree of convenience for patients. Medical record keeping and unified patient monitoring features make this solution extremely useful for physicians and administrative staff alike. Telemedicine apps also aid doctors in efficiently managing their time.
Considering the extensive range of benefits offered by this technology, it is expected to bring about a paradigm shift in the future of healthcare! Watch this space for more insights on eHealth and telemedicine.



